Us Map Of Fault Lines

The United States is home to a diverse range of geological features, including numerous fault lines that crisscross the country. These fault lines are areas of significant seismic activity, where the Earth's crust is being stretched, pulled, or pushed, resulting in the release of energy in the form of earthquakes. In this article, we will explore the US map of fault lines, highlighting the major fault lines, their locations, and the potential risks associated with them.
Major Fault Lines in the United States
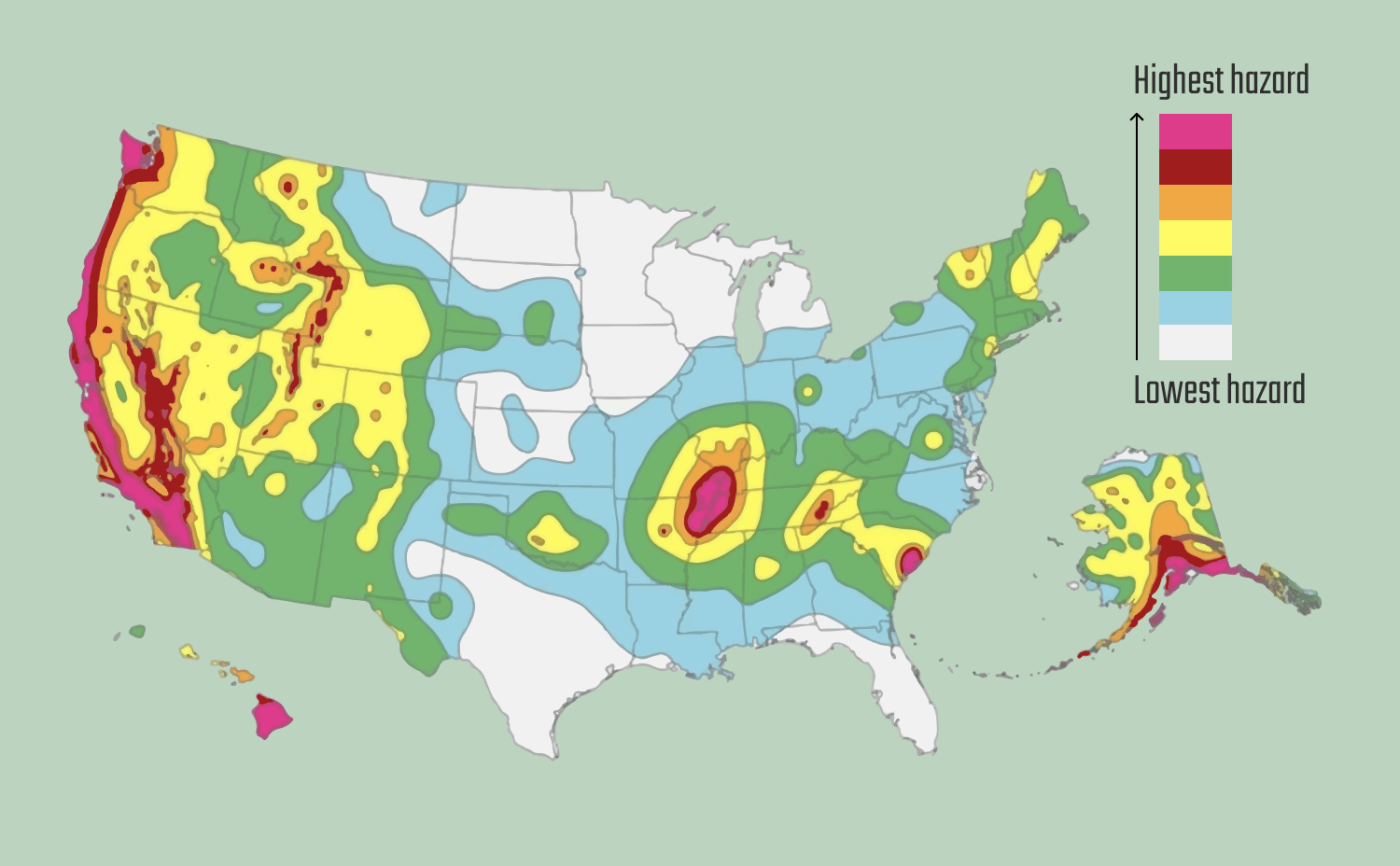
The United States has several major fault lines, including the San Andreas Fault, the Cascadia Subduction Zone, and the New Madrid Seismic Zone. These fault lines are responsible for some of the most significant earthquakes in the country’s history.
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a 1,200-kilometer-long transform fault that runs through California, from the Mendocino Triple Junction in the north to the Salton Sea in the south. It is one of the most active fault lines in the world and is responsible for many significant earthquakes in California, including the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake.
Cascadia Subduction Zone
The Cascadia Subduction Zone is a 700-kilometer-long fault that runs along the Pacific coast of North America, from Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California. It is a subduction zone, where one tectonic plate is being pushed beneath another, resulting in significant seismic activity. The Cascadia Subduction Zone is capable of producing massive earthquakes, including a potential magnitude 9.0 earthquake that could affect the entire Pacific Northwest.
New Madrid Seismic Zone
The New Madrid Seismic Zone is a region of high seismic activity that covers parts of eight states, including Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee, Oklahoma, and Mississippi. It is located in the central United States and is thought to be a rift zone, where the North American plate is being pulled apart. The New Madrid Seismic Zone is responsible for several significant earthquakes, including the 1811-1812 New Madrid earthquakes, which were some of the largest in US history.
| Fault Line | Location | Length (km) |
|---|---|---|
| San Andreas Fault | California | 1,200 |
| Cascadia Subduction Zone | Pacific coast of North America | 700 |
| New Madrid Seismic Zone | Central United States | 350 |

Other Significant Fault Lines in the United States
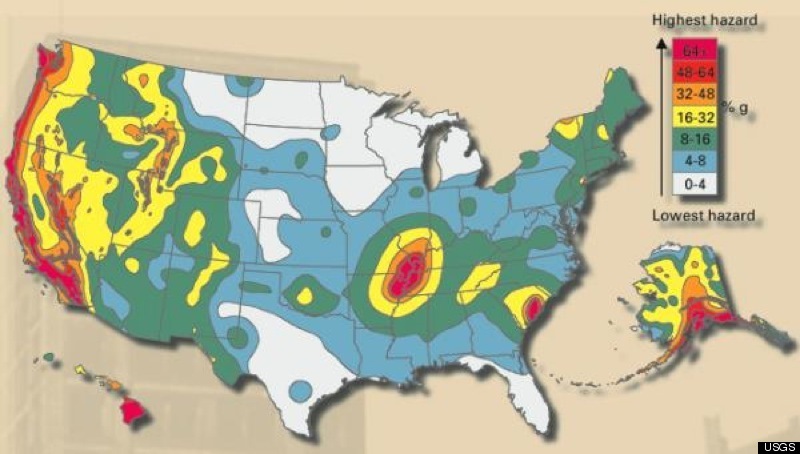
In addition to the San Andreas Fault, the Cascadia Subduction Zone, and the New Madrid Seismic Zone, there are several other significant fault lines in the United States. These include the Hayward Fault, the Calaveras Fault, and the Denali Fault, among others.
Hayward Fault
The Hayward Fault is a 120-kilometer-long transform fault that runs through the San Francisco Bay Area, from San Jose to Berkeley. It is considered one of the most hazardous fault lines in the United States, with a potential for a magnitude 7.0 earthquake.
Calaveras Fault
The Calaveras Fault is a 120-kilometer-long transform fault that runs through the San Francisco Bay Area, from San Jose to Stockton. It is thought to be a significant contributor to the seismic hazard in the region, with a potential for a magnitude 7.0 earthquake.
Denali Fault
The Denali Fault is a 1,200-kilometer-long transform fault that runs through Alaska, from the Alaska Peninsula to the Canadian border. It is one of the most significant fault lines in North America, with a potential for a magnitude 8.0 earthquake.
- San Andreas Fault: 1,200 km long, runs through California
- Cascadia Subduction Zone: 700 km long, runs along the Pacific coast of North America
- New Madrid Seismic Zone: 350 km long, covers parts of eight states in the central United States
- Hayward Fault: 120 km long, runs through the San Francisco Bay Area
- Calaveras Fault: 120 km long, runs through the San Francisco Bay Area
- Denali Fault: 1,200 km long, runs through Alaska
What is the most significant fault line in the United States?
+The San Andreas Fault is considered one of the most significant fault lines in the United States, with a potential for a magnitude 8.0 earthquake.
What is the Cascadia Subduction Zone?
+The Cascadia Subduction Zone is a 700-kilometer-long fault that runs along the Pacific coast of North America, from Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California. It is a subduction zone, where one tectonic plate is being pushed beneath another, resulting in significant seismic activity.
What is the New Madrid Seismic Zone?
+The New Madrid Seismic Zone is a region of high seismic activity that covers parts of eight states, including Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee, Oklahoma, and Mississippi. It is thought to be a rift zone, where the North American plate is being pulled apart.

