State Of Florida Elevation Map
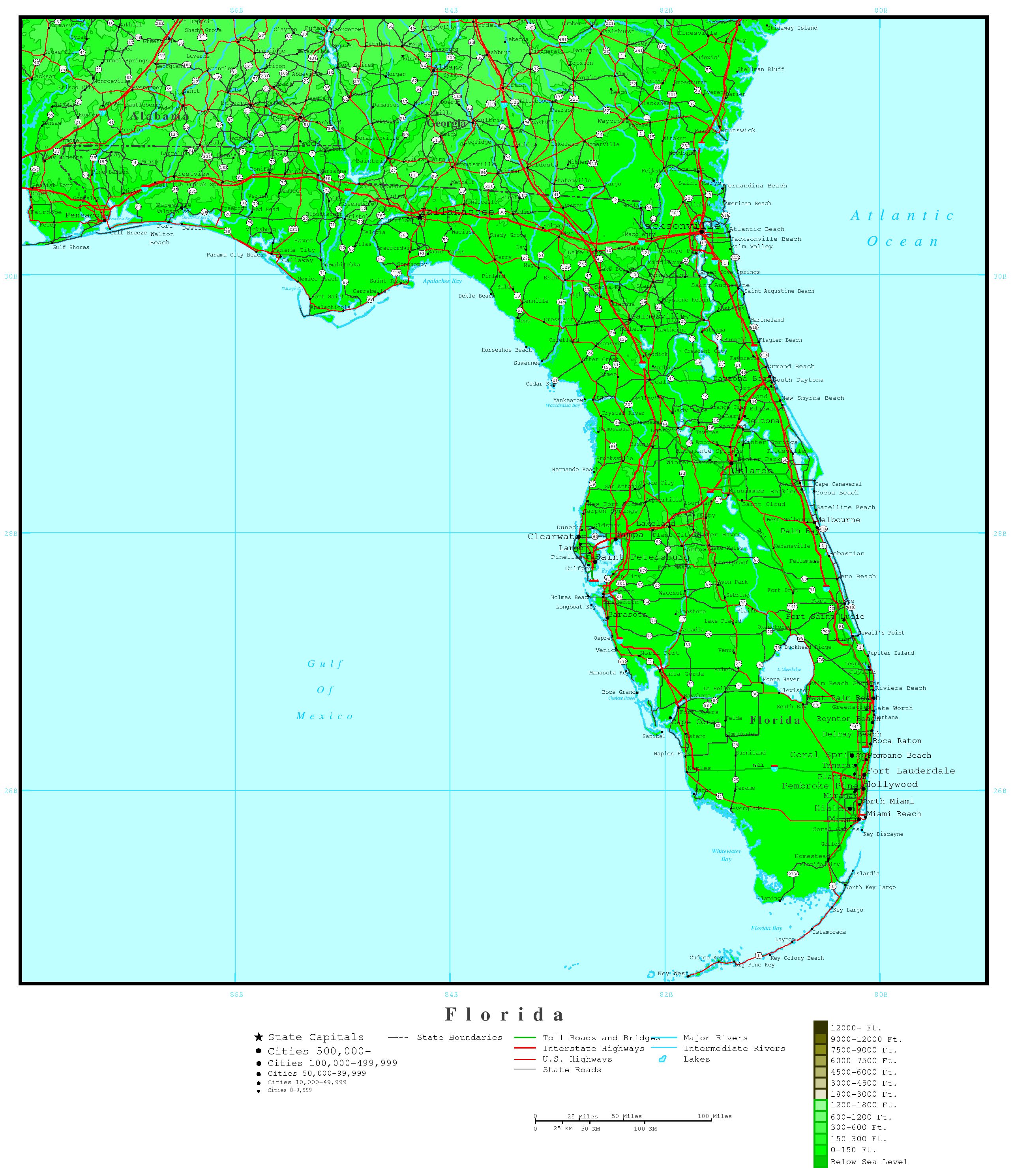
The State of Florida is known for its unique geography, with a diverse range of elevations that span from sea level to over 300 feet above sea level. The Florida elevation map is a vital tool for understanding the state's topography and its implications for various aspects of life, including agriculture, urban planning, and environmental conservation.
Overview of Florida’s Elevation
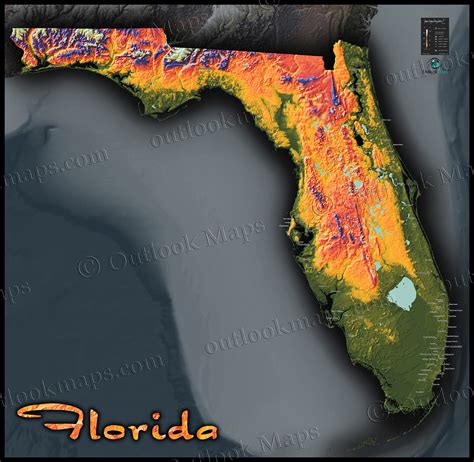
Florida’s elevation is generally low, with an average elevation of around 100 feet above sea level. The state’s highest point is Britton Hill, located in Lakewood, Florida, which stands at an elevation of 345 feet above sea level. The lowest point in Florida is the Atlantic Ocean, which borders the state to the east. The elevation of Florida varies from north to south, with the northern parts of the state tend to be higher in elevation than the southern parts.
Elevation Zones in Florida
Florida can be divided into several elevation zones, each with its unique characteristics and features. The main elevation zones in Florida include:
- Coastal Plains: This zone includes the areas along the coast, which are generally at or near sea level. The coastal plains are characterized by flat to gently sloping terrain and are often prone to flooding.
- Central Highlands: This zone includes the central part of the state, which is characterized by rolling hills and elevations ranging from 100 to 200 feet above sea level. The central highlands are home to many of Florida's lakes, rivers, and wetlands.
- Western Highlands: This zone includes the western part of the state, which is characterized by higher elevations and more rugged terrain. The western highlands are home to many of Florida's highest points, including Britton Hill.
The elevation zones in Florida have a significant impact on the state's climate, soil, and vegetation. For example, the coastal plains are generally warmer and more humid than the central highlands, which are cooler and drier. The western highlands are characterized by a more temperate climate, with cooler winters and warmer summers.
| Elevation Zone | Average Elevation | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Coastal Plains | 0-50 feet | Flat to gently sloping terrain, prone to flooding |
| Central Highlands | 100-200 feet | Rolling hills, many lakes, rivers, and wetlands |
| Western Highlands | 200-300 feet | Higher elevations, more rugged terrain, cooler and drier climate |
Implications of Florida’s Elevation
The elevation of Florida has significant implications for various aspects of life, including agriculture, urban planning, and environmental conservation. For example, the state’s low elevation makes it prone to flooding, particularly in the coastal plains. The elevation also affects the state’s climate, with the coastal plains tend to be warmer and more humid than the central highlands.
Agricultural Implications
The elevation of Florida has a significant impact on the state’s agriculture, with many crops being affected by the state’s low elevation and high water table. For example, citrus crops are often grown in the central highlands, where the soil is better drained and the climate is cooler and drier. The coastal plains, on the other hand, are often used for growing crops such as sugarcane and tomatoes, which are more tolerant of flooding and high water tables.
Urban Planning Implications
The elevation of Florida also has significant implications for urban planning, with many cities and towns being located in the coastal plains. The low elevation of these areas makes them prone to flooding, particularly during heavy rainfall events or storms. As a result, urban planners must take the elevation of Florida into account when designing and building cities and towns, using techniques such as flood-control measures and elevated construction to mitigate the impacts of flooding.
What is the highest point in Florida?
+The highest point in Florida is Britton Hill, located in Lakewood, Florida, which stands at an elevation of 345 feet above sea level.
What is the lowest point in Florida?
+The lowest point in Florida is the Atlantic Ocean, which borders the state to the east.
How does the elevation of Florida affect the state’s climate?
+The elevation of Florida affects the state’s climate, with the coastal plains tend to be warmer and more humid than the central highlands. The western highlands are characterized by a more temperate climate, with cooler winters and warmer summers.


